Understanding Trichomoniasis and Urethritis
When it comes to discussing sexual health, it's important to be aware of the various infections and conditions that can affect both men and women. Trichomoniasis and urethritis are two such infections that are often misunderstood or overlooked. In this article, we'll delve into the connection between these two conditions and share important information to help you maintain your sexual health.
Before we explore the connection between trichomoniasis and urethritis, let's first understand what each of these conditions entails.
What is Trichomoniasis?
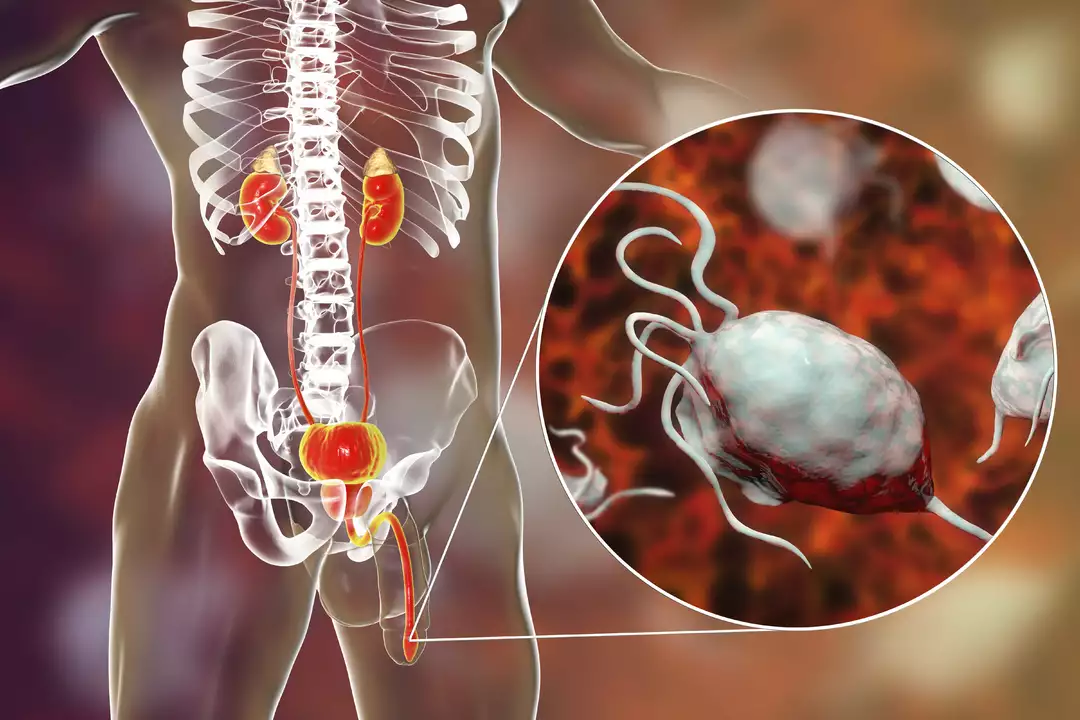
Trichomoniasis, also known as "trich," is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by a parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis. This infection affects both men and women, with women being more likely to experience symptoms. The symptoms of trichomoniasis can include itching, burning, and discharge in women, and discomfort during urination or ejaculation in men. However, many individuals with trichomoniasis may not show any symptoms at all.
Trichomoniasis can be easily treated with antibiotics, but if left untreated, it can lead to more serious health issues, such as an increased risk of contracting other STIs or complications during pregnancy.
What is Urethritis?
Urethritis is an inflammation of the urethra, which is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. This condition can be caused by various factors, including bacterial infections, viral infections, or even injury to the urethra. Symptoms of urethritis can include painful urination, frequent urination, and discharge from the urethra.
The treatment for urethritis depends on the underlying cause, with antibiotics often prescribed for bacterial infections, and antiviral medications used for viral infections.
The Connection Between Trichomoniasis and Urethritis
Now that we have a basic understanding of trichomoniasis and urethritis, let's explore the connection between these two conditions. Trichomoniasis, as mentioned earlier, is caused by the Trichomonas vaginalis parasite. This parasite can also cause urethritis in both men and women by infecting the urethra.
When an individual has both trichomoniasis and urethritis, the symptoms can be more severe and harder to manage. Additionally, having one of these conditions can increase the risk of developing the other, as the inflammation caused by urethritis can make it easier for the Trichomonas vaginalis parasite to establish an infection.
Diagnosing Trichomoniasis and Urethritis
Diagnosing trichomoniasis and urethritis can be done through a series of laboratory tests. For trichomoniasis, a healthcare provider may collect a sample of vaginal or penile discharge to examine under a microscope, or may send the sample for further testing in a lab. In the case of urethritis, a swab of the urethra may be collected and sent for lab testing to determine the cause of the inflammation.
It's important to get tested if you suspect that you may have either trichomoniasis or urethritis, as early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and reduce the risk of spreading these infections to your sexual partners.
Treatment Options for Trichomoniasis and Urethritis
Treating trichomoniasis and urethritis depends on the cause of the infection. In the case of trichomoniasis, antibiotics such as metronidazole or tinidazole are typically prescribed. It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics to ensure that the infection is fully treated.
For urethritis, treatment will depend on the underlying cause. If the inflammation is due to a bacterial infection, antibiotics will be prescribed, while antiviral medications will be used if the cause is viral. It's essential to follow your healthcare provider's recommendations for treatment to ensure a full recovery.
Preventing Trichomoniasis and Urethritis
Prevention is key when it comes to maintaining your sexual health and avoiding infections like trichomoniasis and urethritis. Some effective prevention strategies include practicing safe sex by using condoms consistently and correctly, limiting the number of sexual partners, and getting regularly tested for STIs.
It's also important to maintain good hygiene, such as urinating after sexual intercourse and keeping the genital area clean and dry. Additionally, being open with your sexual partners about your sexual health can help prevent the spread of infections.
Complications of Untreated Trichomoniasis and Urethritis
If left untreated, trichomoniasis and urethritis can lead to various complications. For women, untreated trichomoniasis can increase the risk of contracting other STIs, such as HIV, and can cause complications during pregnancy, such as premature birth or low birth weight.
For men, untreated urethritis can lead to more severe infections, such as prostatitis or epididymitis, and can potentially cause fertility issues. Additionally, untreated trichomoniasis and urethritis can increase the risk of developing pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women, which can cause chronic pain and fertility issues.
When to See a Healthcare Provider
If you suspect that you may have trichomoniasis or urethritis, it's essential to see a healthcare provider as soon as possible. Symptoms such as discharge, painful urination, or itching and burning in the genital area should not be ignored, as these can be indicative of an infection.
It's also crucial to seek medical attention if you have been diagnosed with one of these conditions and your symptoms have not improved after completing the prescribed treatment. Your healthcare provider can help determine the cause of your symptoms and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Conclusion
Trichomoniasis and urethritis are two common sexually transmitted infections that can cause discomfort and complications if left untreated. By understanding the connection between these conditions, practicing safe sex, and seeking medical attention when needed, you can protect yourself and your sexual partners from these infections and maintain a healthy sex life.

katerine rose
May 7, 2023 AT 06:19Iris Schaper
May 7, 2023 AT 17:45it's wild how a tiny parasite can make you feel like your body betrayed you. and the worst part? you might not even know you have it. no symptoms, no drama, just... quietly spreading. like a silent roommate who never does dishes but leaves weird stains on the couch.
and then you get tested, and boom-your whole relationship timeline flashes in front of you. 'oh so that one time in college... yeah that was probably it.'
why is it that the most common sti is also the most ignored? maybe because it doesn't come with a movie trailer or a celebrity PSA. just a prescription for metronidazole and the shame of admitting you didn't use a condom that one time.
we need more honest conversations. not just 'be safe' but 'here's what actually happens when you don't'. trich doesn't care if you're educated or religious or woke-it just wants a warm place to multiply. and we're letting it win by pretending it doesn't exist.
Selma Cey
May 8, 2023 AT 18:24Francis Pascoe
May 8, 2023 AT 20:55Richa Shukla
May 9, 2023 AT 13:05Chris Rowe
May 11, 2023 AT 03:54Sushmita S
May 11, 2023 AT 21:14AnneMarie Carroll
May 13, 2023 AT 09:05John K
May 14, 2023 AT 05:50Laura Anderson
May 14, 2023 AT 11:57Avis Gilmer-McAlexander
May 14, 2023 AT 22:22Jerry Erot
May 15, 2023 AT 12:48Fay naf
May 16, 2023 AT 08:07ANTHONY SANCHEZ RAMOS
May 17, 2023 AT 21:16